文章目录(Table of Contents)
简介
目前有许多实验来比较不同「视觉编码」对感知准确率的影响,但是很少有研究来研究「冗余编码」的优势【While a number of studies in data visualization have investigated perceptual accuracies of visual encoding types, far less is known on the often assumed benefits of redundant encoding, where multiple visual properties represent the same data】。
在这项研究中,我们进行实验来测量位置、长度、角度和面积上冗余编码值的感知准确性和速度【In this study, we conduct experiments to measure the perceptual accuracy and speed of redundant encodings of value on position, length, angle, and area】
实验结果表明,「冗余编码」对人们判断的准确率和速度没有太大的影响,不会变差也不会变好【Our results demonstrate that the redundant addition of value to more accurate encoding types neither enhances nor detracts from perceptual judgments】。
我们得出结论,冗余值编码的中立性可以在设计师的决策中发挥重要作用,并在不影响准确性或速度的情况下为信息图增加视觉兴趣【We conclude that the neutrality of redundant value encoding can serve an important role in a designer's decision making and add visual interest to an infographic without impeding accuracy or speed】。
参考资料
另外一篇关于「冗余编码」的文章,Redundant Encoding Strengthens Segmentation and Grouping in Visual Displays of Data。
需要注意的是,这篇文章产生的结论与上面的文章是相反的,因为他们做的实验是不一样的。这里的准确率其实是「冗余编码」是否可以提高预测百分比的准确率,而没有去比较「冗余编码」帮助人们更好的对不同类别进行分类。
Introduction
可视化的核心是将数据编码为可视化元素(visual properties, visual variables),这些可视化元素包含,position、length,angle,area,color。关于可视化元素的实验,Cleveland and McGill (1984) 进行了许多的研究,这些研究也被后续研究所确认 (Heer & Bostock, 2010)。
在实际生活中,「冗余编码」已经被广泛的使用。例如下图中线条的粗细和线条的角度(slope of the line and the thickness of the line)都用来表示不同州疫苗的覆盖率(vaccination coverage across different states)
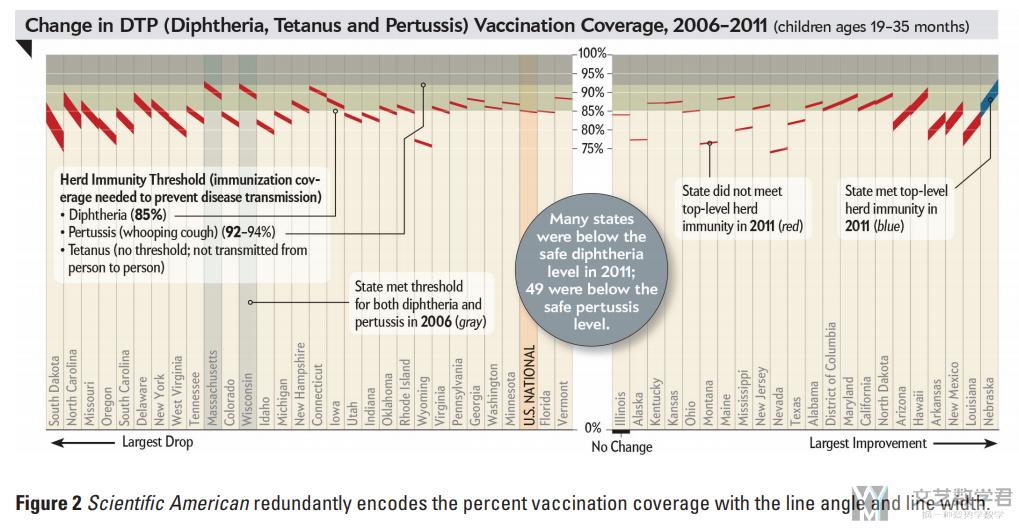
存在的问题
虽然现在有研究单个可视化元素,但是很少研究这些元素如何相互作用的【questions remain about how these visual variables can interact with each other】。
也很少有研究去探讨 redundant encoding 的作用【Very little has been done to investigate the efficacy of redundant encoding】。
Redundant encoding 是指使用两种或以上的可视化元素来对数据进行编码【Redundant encoding refers to the encoding of a single piece of data into two or more visual variables】。
目前虽然有一些研究说明「冗余编码」的好处,但是这些研究都缺少数据【What are missing from this conversation are experimental data that can shed light on the assumed efficacy of redundant encoding in data visualizations】。
本文的创新点
本文会通过实验来验证「冗余编码」对判断的准确度和速度是否有影响【The aim of this study is to attempt to fill that research gap and explore the interactions between primary visual encodings and secondary (redundant) encodings and to determine what effect if any, redundant encoding has on the accuracy and speed of perceptual judgments】。
当我们了解「冗余编码」是否对结果产生影响之后,可以对媒体的可视化产生帮助【It has immediate implications on the development of visualizations in the media by offering empirical data on which communication professionals can base sound design decisions】
Research Goal
新闻图表中,读者最常见的任务之一就是进行比较。例如,条形图依赖于长度估计,饼图依赖于角度估计【News graphics present charts where one of the most common tasks for the reader is to make comparisons. Comparing one visual to another involves an estimation of proportion based on the particular visual encoding chosen. For example, bar charts rely on an estimation of length, and pie charts rely on an estimation of angle】。
为了研究「冗余编码」,本文提出了以下的两个研究问题:
- 使用「冗余编码」是否会对判断的准确率产生影响【RQ1: Does a secondary (redundant) encoding of a separable visual variable, specifically value, produce any beneficial or harmful effect on the accuracy of proportional judgments for graphs encoded with different primary encodings?】。
- 使用「冗余编码」是否会对判断的速度产生影响【RQ2: Does a secondary (redundant) encoding of a separable visual variable, specifically value, have any effect on the speed of judgment tasks for graphs encoded with different primary encodings? 】。
下表列出了四种「可视化编码」,从上到下代表对准确率的影响(结论来自于 Cleveland and McGill),例如 position 是最准确的编码方式。
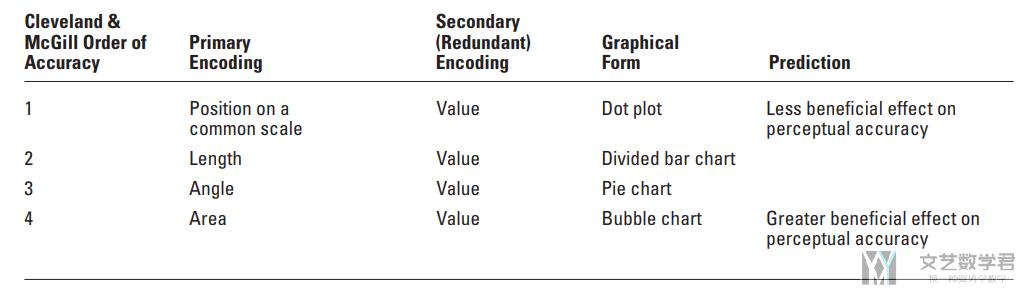
我们使用的冗余编码是 value(shades of gray)。在 Cleveland and McGill 的实验中,value 的准确率是最低的,比 Area 还要低。
我们预期的是:
- 对于更精确的编码(如位置),值的附加好处是最小的。也就是读者将忽略值编码而选择位置这个「可视化编码」【Hence, we posit that the additive benefit of value to a far more accurate encoding, such as position, is minimal. Readers will disregard the value encoding in favor of position】。
- 然而,相对较不精确的编码(如面积)而言,附加值的好处更大,实验结果应该表明这种差异。在区域判断方面有更多困难的读者可能会利用值提供的冗余编码【The additive benefit of value to a less accurate encoding such as area, however, is proportionally greater, and experimental results should show that difference. Readers having more trouble with area judgments may leverage the redundant encoding afforded by value】。
Method
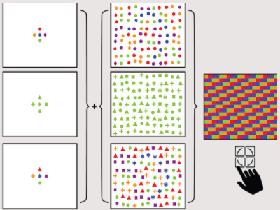
为了验证上面的结论(to test the accuracy and speed of graphical perception of redundant encodings with four common visual encoding types),本文作者设计了下面的四组实验(如下图所示):
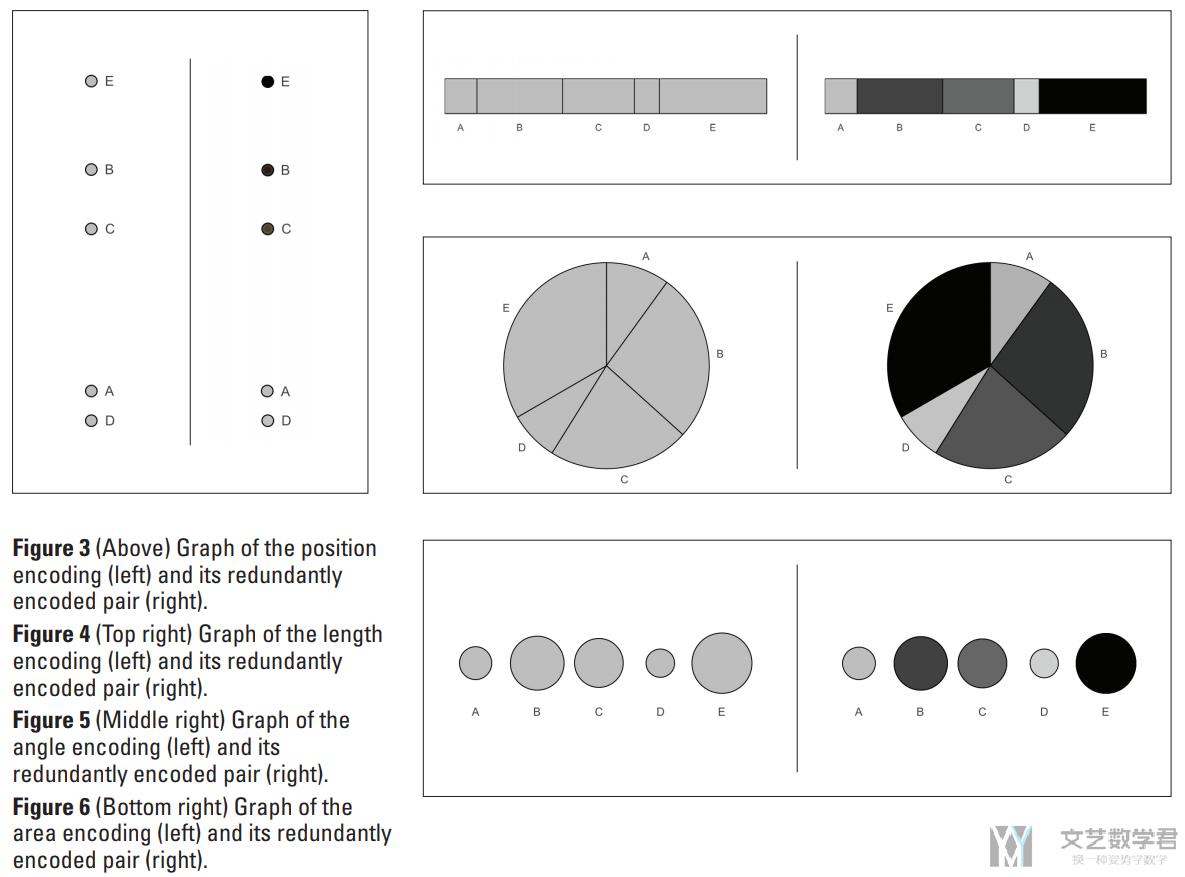
下面是对于上面图的一些介绍:
- 上面是四组实验,分别对应四种不同的 visual encoding 的方式,分别是 position,length,angle,area。
- 每一幅图中包含五类,分别标记为 A,B,C,D,E,之后读者需要估计这五部分的占比。
- 对于「冗余编码」我们选择了不同的灰度级别。使用了一个值(亮度)的线性刻度,其中纯黑色代表100%,纯白色代表0%。
- 上面四组实验,每组实验包含两类(有冗余编码和没有冗余编码),每个七张图片,共有 4*2*7=56 个实验图片,每一个实验图片做了 30 次实验,一共有 30*56=1680 个实验回复【 We requested 30 assignments for each chart for a total of 1,680 total survey responses】。
- 实验要求实验者快速回答出「一个类别占最大类别的百分比」。在回答之前,实验者会看到下图所示的实验介绍【they make a quick visual judgment of what the percentage of one category is to the largest. Subjects were instructed that their answers were to be a number from 1 to 100】。

在介绍完实验之后,实验者开始回答问题。在每一个问卷中,都会包含一个题目,What percentage the category was of itself. 用这个问题来确认实验者是否理解实验的含义【The question served as a check to verify that the subject was paying attention and understood the survey instructions】。
下图是一个问卷的例子:

Results
本文作者使用了与 Cleveland and McGills 一样的方法来计算误差(Log Absolute Error):
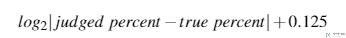
作者还计算了 midmeans 来作为指标,他是通过计算数据集中第二和第三四分位数的平均值得到的,这个值用来作为对异常值不敏感的稳健量【The midmean is the average of the second and third quartile of the data set, used by both Cleveland and McGill (1984) and Heer and Bostock (2010) as a robust measure less susceptible to outliers】。
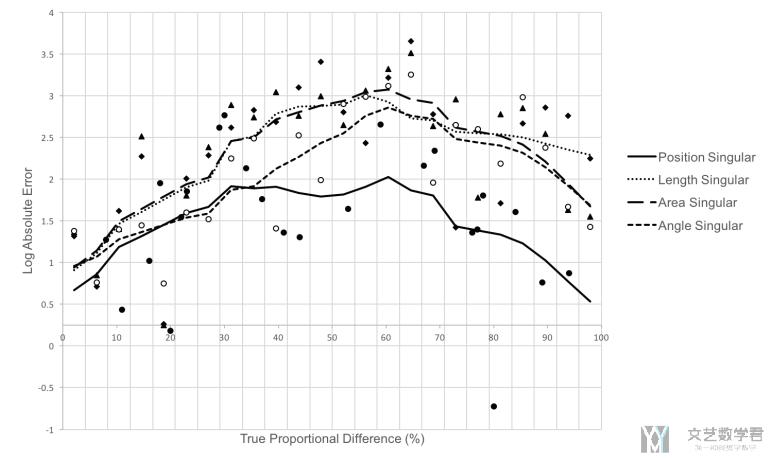
真实值与 Log Absolute Error 的关系如下图所示,首先是不使用「冗余编码」的结果
接着是使用了「冗余编码」的结果(这里 x 轴是 Log Absolute Error,y 轴是真实的比例):
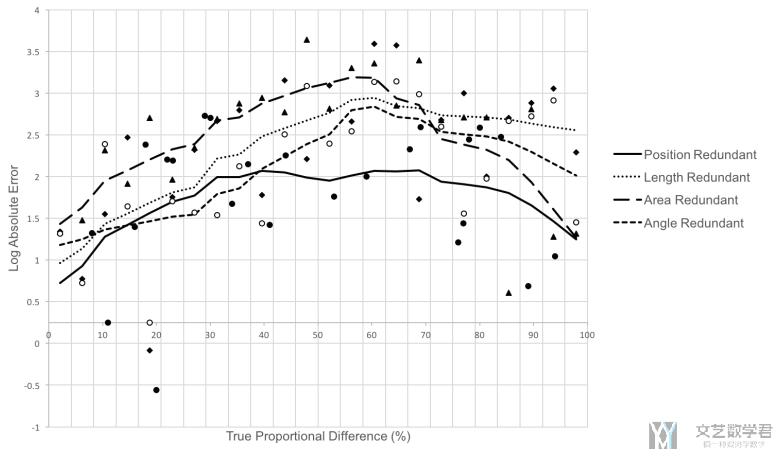
可以看到,当真实的比例较小和较大的时候,模型是预测的比较准确的(也就是两端的 Loss 值比较低) 【Perceptual accuracy is greater when judging very small or very large percentages】
Accuracy of Judgements
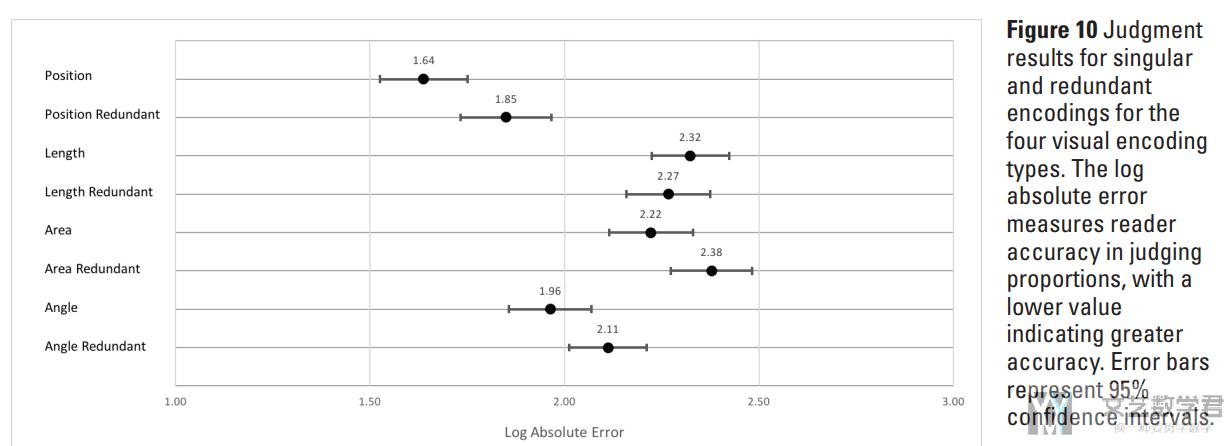
接着我们计算 mean log errors 包含 95% 的置信区间,结果如下图所示:
其中:
- 在测试的四种视觉编码类型中,通过位置判断比例被证明是最准确的。这个结果与 Cleveland and McGill (1984) 的研究结果是相似的【Judging proportions with position was shown to be the most accurate among the four visual encoding types tested】。
- 用角度(angle)判断比例比用面积(area)更准确,这也与 Bostock and Heer (2010) 对角度和面积的发现一致【Judging proportions with angles was more accurate than with area, which is also consistent with Bostock and Heer’s (2010) findings for angle and area】。
- 在我们的研究中,用长度(length)判断与使用面积(area)判断结果相似。 这与 Cleveland and McGill 以及 Bostock and Heer 的长度实验与角度实验更相似【Judgments with length ranked similarly to area on the low end of accuracy in our study. Cleveland and McGill’s and Bostock and Heer’s length experiments were more similar to angle】。
- 四种主要编码类型(位置、长度、角度和面积)中的每一种的冗余编码在判断精度上都没有表现出任何显着差异【The redundant encodings for each of the four types of primary encoding types (position, length, angle, and area) did not show any significant difference in judgment accuracy】。
Speed of Judgements
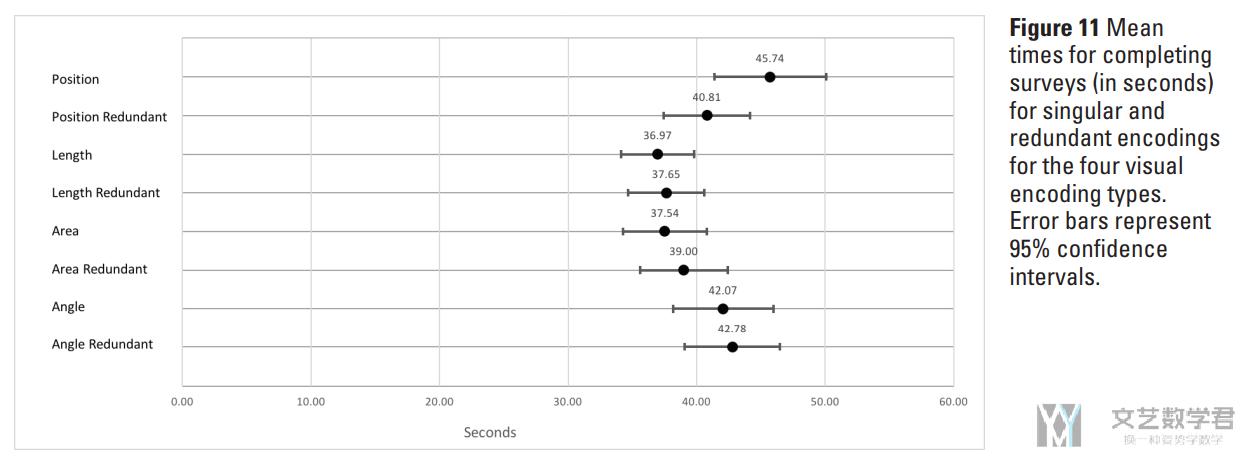
接着是不同类型实验的速度(时间)的比较:
其中:
- 按照位置编码(position)花费的时间是最长的;
- 按照长度编码(length)花费的时间是最短的;
- 带有「冗余编码」的实验结果与不带「冗余编码」没有体现出明显的不同【Charts with redundant encodings showed no significant differences in completion time】;
Discussion(实验结果的解释和作者提出的疑问)
接下来是对上面实验结果的一些讨论:
- 使用单一编码的结果与之前的论文结果相似。 位置(position)被列为最准确的比例判断视觉编码。 角度(angle) 的表现优于长度(length)。
- 使用「冗余编码」不会对任何图形类型产生任何可测量的好处,这与我们的假设相矛盾,即 value 会对不太准确的编码类型产生更大的有益影响,而对更精确的编码类型产生较小的有益影响【Redundant encoding with the addition of the separable visual variable of value did not result in any measurable benefit for any of the graph types, contradicting our hypothesis that value would have a greater beneficial effect on less accurate encoding types and a lesser beneficial effect on more accurate encoding types】。
- 对于反应时间来说,总体上没有明显的差别。表示「冗余编码」没有提供帮助,但是也没有影响读者的判断【The mean times for processing each chart type did not vary significantly, implying that the secondary encoding was neither an aid to faster decoding nor a distraction to the decoding process】。
下面是作者提出的一些疑问:
- 作者疑惑读者是如何利用「冗余编码」的,例如人们是否会只使用一个有利的编码,而过滤掉最不准确的编码【Although our survey instructions explicitly stated that the data were encoded with both types of visuals, we surmise that readers filtered out the least helpful (least accurate) of the encodings—the value—and focused instead on the primary encoding to perform the task at hand】。
- 基于上面的猜测,如果人们只使用一个有利的编码,那么是否会出现当两种编码方式表现相同时,人们的准确率反而会下降【If the discriminability in accuracy of the two visual encodings become very close, would reader perception see a redundancy gain because of a gestalt effect or a drop in accuracy because of visual interference】
- 对于「冗余编码」适合的任务类型。我们的结果表明,可分离变量的冗余增益可能仅适用于形状和颜色、排序和分类任务 --> 这里指出「冗余编码」可能不适合这里预测 proportional 的任务,而是适合其他的任务。
- 对于处理的时间,可以看到最准确的编码(位置)的处理时间也最长,而处理速度最快的编码(长度)是最不准确的编码之一【It is interesting to note that the most accurate encoding (position) also took the longest to process, while the quickest to process (length) was one of the least accurate】。
- 那么是否会存在这样的可能,因为视觉编码(位置)迫使人们花费更多时间去理解,所以准确率比较高呢【The question arises: Is the greater accuracy of position inherent in its visual encoding or because the form forces readers to spend more time on the decoding process, with concomitant greater accuracy】。
Conclusion
- 我们得出的结论是,在用位置(position)、长度(length)、角度(angle)或面积(area)这四组数据可视化中,冗余编码对于比例判断任务没有明显的好处【We conclude that value, specifically, has no discernible benefits or costs to proportional judgment tasks in data visualizations redundantly encoded with position, length, angle, or area】。
- 冗余编码对准确性或判断速度没有显着影响【Redundant encoding showed no significant effects on either accuracy or on judgment speed】。
- 本文得出结论,因为「冗余编码」不会影响数据可视化的效果,因此使数据可视化的设计者和开发人员能够将冗余编码中的价值用于纯粹的美学目的【Though limited in scope, the conclusion actually frees up designers and developers of data visualizations to use value in redundant encoding for purely aesthetic purposes without compromising the efficacy of the primary encoding】。
我们的结论反驳了 Tufte 支持者长期以来的主张,即在数据可视化中“少即是多”,而“更多”不利于信息交流。 相反,「冗余特征」形式存在的更多信息可以潜在地增强设计,而不会削弱图形感知的完整性【Our conclusion counters long-held assertions from advocates of Tufte that “less is more” in data visualizations and that “more” does disservice to the communication of information. On the contrary, more information in the form of redundant variations of value can potentially enhance design without weakening the integrity of graphic perception】。
- 微信公众号
- 关注微信公众号
-

- QQ群
- 我们的QQ群号
-



评论