文章目录(Table of Contents)
Reinforcement learning-based multi-agent system for network traffic signal control
这一篇是使用强化学习(reinforcement learning)来控制交通信号灯。这一篇主要介绍交通信号灯之间的协作。文章的具体信息如下所示:
- Arel, Itamar, Cong Liu, Tom Urbanik, and Airton G. Kohls. "Reinforcement learning-based multi-agent system for network traffic signal control." IET Intelligent Transport Systems 4, no. 2 (2010): 128-135.
一句话概括如何在不同交通灯之间协作:让不同路口的信息可以在不同的交通灯之间进行共享;
传统方法的不足
- Conventional deterministic traffic management systems fail to scale with respect to scheduling large networks of signals in urban settings, largely due to the lack of a long-term reward policy.
- In a heavy-loaded multi-intersection traffic network, congestion occurring in a single lane does not only impact upstream traffic, but also the other intersections.(单个车道的拥堵会影响其他的路口)
- Thus, an efficient scheduling method that maximises a long-term reward and that can control a dynamic and complex traffic environment is highly desired.(需要可以最大限度的提高长期回报)
本文的创新点
- We utilise a multi-agent setting, whereby RL is employed as means of controlling the different intersections in the network. (使用一个multi-agent的强化学习模型, 来同时控制多个路口)
- The coordination factor among the intersection is an obscure object and has a nonlinear relation. The AI intelligent algorithm can compute the inner nonlinear relation which cannot be provided by the traditional approach. (多个路口之间的相互影响是复杂的, 我们使用RL来解决)
- Simulation results clearly indicate that the proposed RL control scheme outperforms the LQF (longest-queue-first) algorithm strategy by yielding a lower delay and cross-blocking frequency, particularly for medium and high traffic arrival rates. (实验结果表明使用RL的效果比传统方法LQF要好)
多个路口同时控制的目标
在说明目标之前, 我们先定义一些术语:
- Traffic throughput(交通吞吐量): average number of vehicles per unit of time successfully traverse the intersection.
- Traffic congestion(交通拥堵): typically occurring in multi-intersection settings, is a condition in which a link is increasingly occupied by queued vehicles. Highly congested intersections often cause cross-blocking whereby vehicles moving upstream fail to cross an intersection due to lack of queuing positions at a designated link.
所以,low traffic throughput 和 high traffic congestion 会造成交通拥堵。所以本模型的目标就是最大化 traffic throughput。
多个路口环境说明
接着看一下本文所使用的环境. 环境如下图所示:
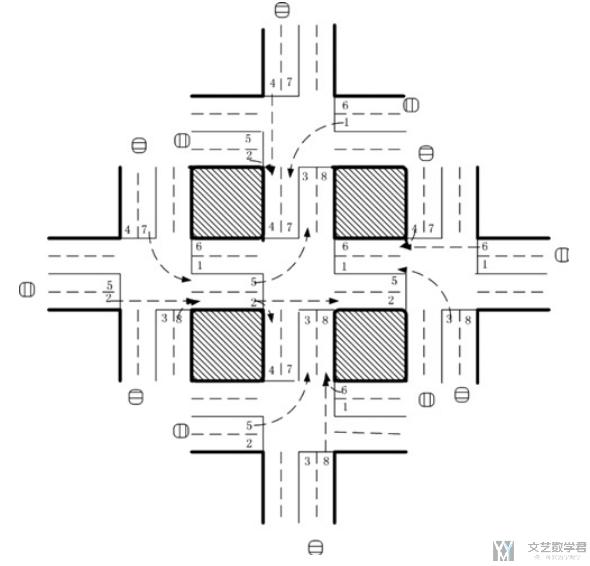
我们简单对上面的环境进行说明:
- 环境描述
- 环境中有5个十字路口, 中间的十字路口是中心路口(central intersection).
- 周围的4个路口被叫做outbound intersections.
- 图中车道数字的含义
- 图中的even number (偶数车道), 车可以直行和右转.
- 图中的odd number (奇数车道), 车可以左转到指定的车道.
- 环境的其他信息
- 一个车道最多有40辆车在进行排队.
- 一个车在离开前, 最多经过一个路口, 或是三个路口(outbound-central-outbound)
- 在multi-agent系统中, 一个agent只能获得他直接的临近位置的信息.
- 在模拟的过程中, new vehicles服从Poisson process来产生. 产生的位置在outbound intersection. 每次排在队伍的最后面.
强化学习每一个元素的对应
- System state
- 从上面的环境介绍的图中可以看到, 一个路口有8 lanes. 于是, 对一个十字路口的state是一个8维的向量, 每一个维度是每一条路的relative traffic flow. (the relative traffic flow is defined as the total delay of vehicles in a lane divided by the average delay at all lanes in the intersection.)
- 对于四个周围的十字路口(outbound intersection agent), 只考虑local traffic statistics.
- 对于与中间的十字路口(central intersection), 他可以获得周围四个outbound intersections的信息.
- Action set
- 在上面的图中, 对于每个lane进行编号, 从1-8.
- 一共有8种action, 分别是{(1,5), (1,6), (2,5), (2,6), (3,7), (3,8), (4,7), (4,8)}. 例如(1,5)表示lane 1和lane 5可以同时通行, 不会有冲突.
- Reward function
- 首先, 我们说一下delay的计算方式: In a real-life application, vehicle delay could be estimated through the application of technological advancements in the field of vehicular sensors and traffic controllers. Advance detector (upstream detectors) actuations can be used to track vehicular arrivals at each intersection approach over time (路口到达的车). Phase change data and saturation headway data can be used to estimate the number of departures from the stop bar over time (路口离开的车). The two flow profiles can then be combined to estimate the queue accumulation on the intersection approach. (到达-离开=队伍长度) The time in queue can be used to estimate delay for each approach and consequently for the entire intersection (queue中每一辆车的等待时间, 就是路口的等待时间).
- 如果当前的delay比过去一段时间的delay要低, 那么reward是正的.
- 如果delay比过去一段时间有所增加, 那么reward是负的.
- 于是reward的定义如下图所示, 其中D_last是过去这个路口的delay; D_current是当前这个路口的delay. 对于central intersection的reward, 需要把周围路口的reward也算进来, 加权.
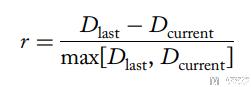
模型的具体设计
在本实验中, 作者只在central intersection中用到了deep Q network. 因为central intersection需要考虑周围的信息, 所以网络的input是5*8=40, 整个网络的结构是40->25->8. 最后output是8维, 是因为一共有8种actions.
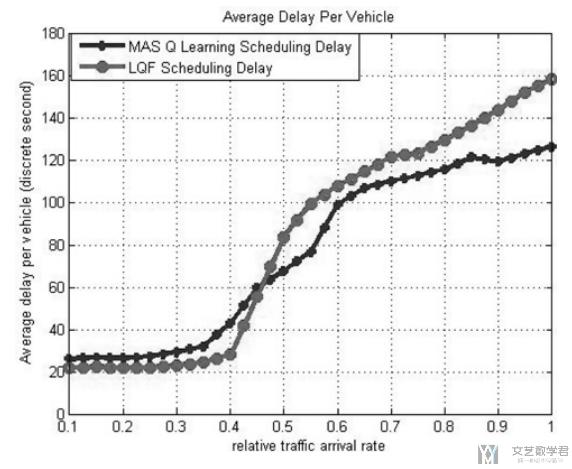
实验结果表示
我们比较了LQF方法和MAS Q Learning的方法. 横轴表示到达率, 可以看到随着汽车越来越多(到达率上升), 此时delay也在上升. 但是当车流量大的时候, MAS Q learning的delay就会比较小.
- 微信公众号
- 关注微信公众号
-

- QQ群
- 我们的QQ群号
-




评论