文章目录(Table of Contents)
入侵检测介绍
IDS : intrusion detection system, 入侵检测系统, 常用的方法有基于 anomaly detection
和 Misuse detection.
Misuse detection
Misuse detection : 特征检测 (误用检测), 基于异常行为模式, 相当于黑名单的机制,
定义出所有异常行为的规则.
Anomaly detection
Anomaly detection : 异常检测, 主要基于正常行为来检测异常行为. 相当于白名单的
机制, 白名单外的均是异常. 现在难点在于如何表达正常行为.
数据集介绍
这一篇会介绍关于KDD99数据集的一些内容。之前使用的时候只是使用了提取的feature,没有具体分析这些特征的含义等,在这里具体说明一下。
对于数据集的分析, 可以查看下面的链接: A Deeper Dive into the NSL-KDD Data Set
异常类型
4种异常类型分别是:
- PROBING(surveillance and probing), 端口监视或扫描,例如port-scan, ping-sweep等。这是一个找目标过程, 进行监视扫描.
- R2L, REMOTE-TO-LOCAL(unauthorized access from a remote machine to a local machine)来自远程主机的未授权访问,例如guessing password; 这是一个远程->本地, 是一个入侵的过程;
- U2R, USER-TO-ROOT(unauthorized access to local superuser privileges by a local unprivileged user)未授权的本地超级用户特权访问,例如buffer overflow attacks;本地提权
- DOS(denial-of-service)拒绝服务攻击,例如ping-of-death, syn flood, smurf等;资源消耗
关于上面的四大类攻击,在KDD99中每一大类中包含下面几种小类的攻击。我们要注意的是,在训练集上出现了24种攻击类型,在测试集上出现了38种攻击类型,也就是说在测试集中出现了14中新的攻击类型(在训练集中没有出现)
详细的攻击类型
详细的攻击的名称见下面的表格。
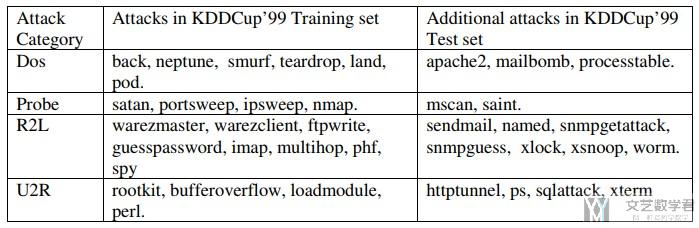
下面是不同攻击在训练集和在测试集上的分布。
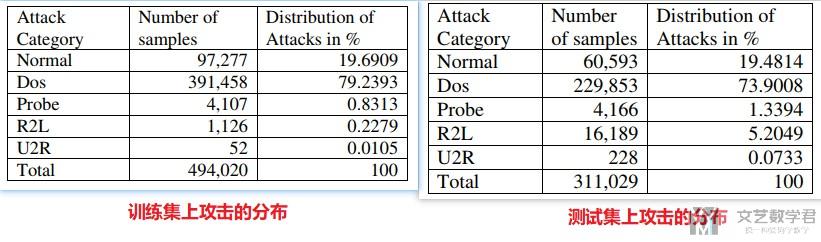
我们可以看到不同攻击的样本在训练集和在测试集上是不平衡的。可以看到R2L攻击在训练集占比0.2%, 但是在测试集上占比为5.2%。
每种攻击类型的介绍
DDoS
- neptune attack(SYN Flood) : To initiate Neptune attack a large number of SYN packets are sent to target machine to exhaust its buffer. Neptune attack never establishes the TCP session resulting in many zero packets in each connection attempt. In our experimentation we have considered 107201 Neptune attacks in altogether. As a result of large number of SYN packets sent by the attacker nodes in case of Neptune attack without actually establishing an actual session there is loss of self similarity and the Hurst values go beyond the required limits. This happens because of same size of incoming bytes for a long duration of time in the traffic. No variation in hurst is used as a signal for attack.
- smurf : Smurf attacks in KDD dataset use ICMP echo request packets directed to IP broadcast addresses from remote locations to create DoS attack. It can be identified by watching large number of Echo requests and replies from the victim machine. The coloumn 'count' values from the dataset can be read and analysed for Smurf attacks. In our experimentation we have considered 280790 Smurf attacks in total.
- Ping-Of-Death (POD) : POD affects older Operating Systems. It uses oversized IP packets to crash, freeze or reboot the system. During the experimentation POD affected none of the victim systems. ICMP packets longer than 64000 bytes can be due to POD attack. In our experimentation we have considered 264 POD attacks in total.
- back : In Back attacks the wrong IP addresses are used by the attacker in the source IP address of the IP packet header. As a result the receiver fails to determine the real attacking node. Since the attacker node cannot be located therefore the attacker cannot be stopped from sending illegitimate packets. The receiver thus gets inundated by unwanted packets and fails to provide service to regular users thus causing denial of service. We have considered 2023 in total.
- teardrop : Teardrop uses overlapping of IP fragments. It causes machines to reboot. This attack affects systems that are still using old versions of Windows and Linux operating systems. In our experimentation we have considered 979 Teardrop attacks in total.
- LAND (Local Area Network Denial) : A LAND attack is a DoS attack under which spoofed packets are sent to the target computer to bring it down. In this attack large number of TCP/SYN packets are sent to the target machine. These attacks are different from the SYN flooding attacks because in these attacks the spoofed IP packets have both the source as well as the destination IP addresses as the target machines IP address. The target machine therefore keeps on sending reply to SYN packets to itself only and thus the buffer gets filled up. The machine therefore fails to provide service to legitimate users.We have considered 21 LAND attacks in total.
DDoS的一些重要的特征。

下面是在test(在测试集)中的DoS攻击的介绍。
下面部分的参考资料
Mailbomb : Mailbomb attacks generally attack email servers. In this type of attack, instead of packets, oversized emails filled with random garbage values are sent to a targeted email server. This generally crashes the email server due to a sudden spike in load and renders them useless until fixed.
Processtable : To launch a process table attack, the client need only open a connection to the server and not send any information. As long as the client holds the connection open, the server's process will occupy a slot in the server's process table.(三次握手完毕, 但是没有发送信息, 这样连接表存储数量会被占满, 从而无法创建新的TCP连接.)
特征描述
TCP连接基本特征
- (1)duration : 连接持续时间,以秒为单位,连续类型。范围是 [0, 58329] 。它的定义是从TCP连接以3次握手建立算起,到FIN/ACK连接结束为止的时间;若为UDP协议类型,则将每个UDP数据包作为一条连接。(数据集中出现大量的duration=0 的情况,是因为该条连接的持续时间不足1秒.)
- (2)protocol_type : 协议类型,离散类型,共有3种:TCP, UDP, ICMP。
- (3)service : 目标主机的网络服务类型,离散类型,共有70种。罗列在下面:aol, auth, bgp, courier, csnet_ns, ctf, daytime, discard, domain, domain_u, echo, eco_i, ecr_i, efs, exec, finger, ftp, ftp_data, gopher, harvest, hostnames, http, http_2784, http_443, http_8001, imap4, IRC, iso_tsap, klogin, kshell, ldap, link, login, mtp, name, netbios_dgm, netbios_ns, netbios_ssn, netstat, nnsp, nntp, ntp_u, other, pm_dump, pop_2, pop_3, printer, private, red_i, remote_job, rje, shell, smtp, sql_net, ssh, sunrpc, supdup, systat, telnet, tftp_u, tim_i, time, urh_i, urp_i, uucp, uucp_path, vmnet, whois, X11, Z39_50。
- (4)flag. 连接正常或错误的状态,离散类型,共11种。OTH, REJ, RSTO, RSTOS0, RSTR, S0, S1, S2, S3, SF, SH。它表示该连接是否按照协议要求开始或完成。例如SF表示连接正常建立并终止;S0表示只接到了SYN请求数据包,而没有后面的SYN/ACK。其中SF表示正常,其他10种都是error。(关于这11种详细的解释,可以查看)
- (5)src_bytes : 从源主机到目标主机的数据的字节数,连续类型,范围是 [0, 1379963888]。
- (6)dst_bytes : 从目标主机到源主机的数据的字节数,连续类型,范围是 [0. 1309937401]。
- (7)land : 若连接来自/送达同一个主机/端口则为1,否则为0,离散类型,0或1。
- (8)wrong_fragment : 错误分段的数量,连续类型,范围是 [0, 3]。
- (9)urgent : 加急包的个数,连续类型,范围是[0, 14]。
关于flag中十一种状态的解释
参考文章,Description of Kyoto University Benchmark Data,直接搜索就可以搜索到。
- S0: Connection attempt seen, no reply.
- S1: Connection established, not terminated.
- SF: Normal establishment and termination.
- REJ: Connection attempt rejected.
- S2: Connection established and close attempt by originator seen (but no reply from responder).
- S3: Connection established and close attempt by responder seen (but no reply from originator).
- RSTO: Connection established, originator aborted (sent a RST).
- RSTR: Established, responder aborted.
- RSTOS0: Originator sent a SYN followed by a RST, we never saw a SYNACK from the responder.
- RSTRH: Responder sent a SYN ACK followed by a RST, we never saw a SYN from the (purported) originator.
- SH: Originator sent a SYN followed by a FIN, we never saw a SYN ACK from the responder (hence the connection was “half” open).
- SHR: Responder sent a SYN ACK followed by a FIN, we never saw a SYN from the originator.
- OTH: No SYN seen, just midstream traffic (a “partial connection” that was not later closed).
关于上面离散特征具体的值, 可以使用下面的表格进行表示(可以使用较小的表格将所有内容都表示出来):

TCP连接的内容特征
对于U2R和R2L之类的攻击,由于它们不像DoS攻击那样在数据记录中具有频繁序列模式,而一般都是嵌入在数据包的数据负载里面,单一的数据包和正常连接没有什么区别。为了检测这类攻击,Wenke Lee等从数据内容里面抽取了部分可能反映入侵行为的内容特征,如登录失败的次数等。
- (10)hot : 访问系统敏感文件和目录的次数,连续,范围是 [0, 101]。例如访问系统目录,建立或执行程序等。
- (11)num_failed_logins : 登录尝试失败的次数。连续,[0, 5]。
- (12)logged_in : 成功登录则为1,否则为0,离散,0或1。
- (13)num_compromised : compromised条件(**)出现的次数,连续,[0, 7479]。
- (14)root_shell : 若获得root shell 则为1,否则为0,离散,0或1。root_shell是指获得超级用户权限。
- (15)su_attempted : 若出现"su root" 命令则为1,否则为0,离散,0或1。
- (16)num_root : root用户访问次数,连续,[0, 7468]。
- (17)num_file_creations : 文件创建操作的次数,连续,[0, 100]。
- (18)num_shells : 使用shell命令的次数,连续,[0, 5]。
- (19)num_access_files : 访问控制文件的次数,连续,[0, 9]。例如对 /etc/passwd 或 .rhosts 文件的访问。
- (20)num_outbound_cmds : 一个FTP会话中出站连接的次数,连续,0。数据集中这一特征出现次数为0。
- (21)is_hot_login : 登录是否属于“hot”列表(***),是为1,否则为0,离散,0或1。例如超级用户或管理员登录。
- (22)is_guest_login : 若是guest 登录则为1,否则为0,离散,0或1。
基于时间的网络流量统计特征
由于网络攻击事件在时间上有很强的关联性,因此统计出当前连接记录与之前一段时间内的连接记录之间存在的某些联系,可以更好的反映连接之间的关系。
这类特征又分为两种集合:
- 一个是same host特征,只观察在过去两秒内与当前连接有相同目标主机的连接,例如相同的连接数,在这些相同连接与当前连接有相同的服务的连接等等;
- 另一个是same service特征,只观察过去两秒内与当前连接有相同服务的连接,例如这样的连接有多少个,其中有多少出现SYN错误或者REJ错误。
下面是具体的特征列表:
- (23)count. 过去两秒内,与当前连接具有相同的目标主机的连接数,连续,[0, 511]。
- (24)srv_count. 过去两秒内,与当前连接具有相同服务的连接数,连续,[0, 511]。
- (25)serror_rate. 过去两秒内,在与当前连接具有相同目标主机的连接中,出现“SYN” 错误的连接的百分比,连续,[0.00, 1.00]。
- (26)srv_serror_rate. 过去两秒内,在与当前连接具有相同服务的连接中,出现“SYN” 错误的连接的百分比,连续,[0.00, 1.00]。
- (27)rerror_rate. 过去两秒内,在与当前连接具有相同目标主机的连接中,出现“REJ” 错误的连接的百分比,连续,[0.00, 1.00]。
- (28)srv_rerror_rate. 过去两秒内,在与当前连接具有相同服务的连接中,出现“REJ” 错误的连接的百分比,连续,[0.00, 1.00]。
- (29)same_srv_rate. 过去两秒内,在与当前连接具有相同目标主机的连接中,与当前连接具有相同服务的连接的百分比,连续,[0.00, 1.00]。
- (30)diff_srv_rate. 过去两秒内,在与当前连接具有相同目标主机的连接中,与当前连接具有不同服务的连接的百分比,连续,[0.00, 1.00]。
- (31)srv_diff_host_rate. 过去两秒内,在与当前连接具有相同服务的连接中,与当前连接具有不同目标主机的连接的百分比,连续,[0.00, 1.00]。
注意:
- 这一大类特征中, count、serror_rate、rerror_rate、same_srv_rate、diff_srv_rate这5个特征是 same host特征,前提都是与当前连接具有相同目标主机的连接;
- srv_count、srv_serror_rate、srv_rerror_rate、srv_diff_host_rate这4个特征是same service特征,前提都是与当前连接具有相同服务的连接。
基于主机的网络流量统计特征
基于时间的流量统计只是在过去两秒的范围内统计与当前连接之间的关系,而在实际入侵中,有些 Probing攻击使用慢速攻击模式来扫描主机或端口,当它们扫描的频率大于2秒的时候,基于时间的统计方法就无法从数据中找到关联。所以Wenke Lee等按照目标主机进行分类,使用一个具有100个连接的时间窗,统计当前连接之前100个连接记录中与当前连接具有相同目标主机的统计信息。
- (32)dst_host_count. 前100个连接中,与当前连接具有相同目标主机的连接数,连续,[0, 255]。
- (33)dst_host_srv_count. 前100个连接中,与当前连接具有相同目标主机相同服务的连接数,连续,[0, 255]。
- (34)dst_host_same_srv_rate. 前100个连接中,与当前连接具有相同目标主机相同服务的连接所占的百分比,连续,[0.00, 1.00]。
- (35)dst_host_diff_srv_rate. 前100个连接中,与当前连接具有相同目标主机不同服务的连接所占的百分比,连续,[0.00, 1.00]。
- (36)dst_host_same_src_port_rate. 前100个连接中,与当前连接具有相同目标主机相同源端口的连接所占的百分比,连续,[0.00, 1.00]。
- (37)dst_host_srv_diff_host_rate. 前100个连接中,与当前连接具有相同目标主机相同服务的连接中,与当前连接具有不同源主机的连接所占的百分比,连续,[0.00, 1.00]。
- (38)dst_host_serror_rate. 前100个连接中,与当前连接具有相同目标主机的连接中,出现SYN错误的连接所占的百分比,连续,[0.00, 1.00]。
- (39)dst_host_srv_serror_rate. 前100个连接中,与当前连接具有相同目标主机相同服务的连接中,出现SYN错误的连接所占的百分比,连续,[0.00, 1.00]。
- (40)dst_host_rerror_rate. 前100个连接中,与当前连接具有相同目标主机的连接中,出现REJ错误的连接所占的百分比,连续,[0.00, 1.00]。
- (41)dst_host_srv_rerror_rate. 前100个连接中,与当前连接具有相同目标主机相同服务的连接中,出现REJ错误的连接所占的百分比,连续,[0.00, 1.00]。
特征压缩
有一些论文会对NSL-KDD的41维特征进行压缩,找出一些比较重要的特征,从而减少模型训练和预测的时间,在这里简单说一下。
论文一, 2005
Reference : Chen, Yuehui, Ajith Abraham, and Ju Yang. "Feature selection and intrusion detection using hybrid flexible neural tree." International Symposium on Neural Networks. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2005.
本文对每个大类的攻击进行重要特征的提取,结果如下所示
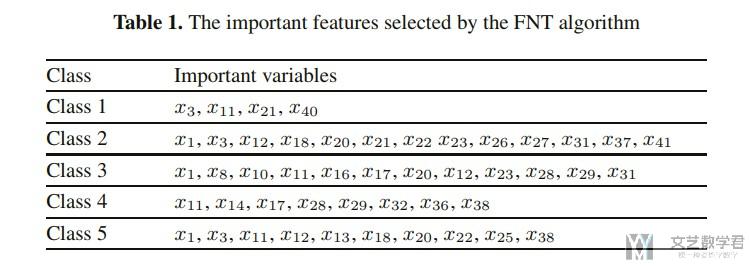
其中, class1表示normal data, class2表示Probe, class3表示dos, class4表示u2r, class5表示r2l.
论文二, 2009
Reference : Staudemeyer, R., and C. W. Omlin. "Feature set reduction for automatic network intrusion detection with machine learning algorithms." Proceedings of the southern African telecommunication networks and applications conference (SATNAC). 2009.
这一篇提取了11个重要的特征,是针对整个数据集进行提取的。
The first six of the selected core features (1,2,3,5,6,8) are base features which can be easily extracted from network traffic with very less overhead. The remaining features (25,33,35,36,40) are time-based and host-based traffic features.
选取的11个特征如下所示:
- 1. duration
- 2. protocol_type
- 3. service
- 5. src_bytes
- 6. dst_bytes
- 8. wrong_fragment
- 25. serror_rate
- 33. dst_host_srv_count
- 35. dst_host_diff_srv_rate
- 36. dst_host_same_src_port_rate
- 40. dst_host_rerror_rate
论文三, 2014
Reference : Staudemeyer, Ralf C., and Christian W. Omlin. "Extracting salient features for network intrusion detection using machine learning methods." South African computer journal 52.1 (2014): 82-96.
这一篇文章使用决策树的方法,对每一大类的攻击分别进行特征的提取。同时通过计算相关系数,将相关系数较高的特征去除,留下少量的特征。
DoS攻击
- 11个重要特征 : 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 23, 29, 36, 38, 39, 40
- 去除高相关性特征, 留下5个 : 3, 4, 5, 29, 39
Probe攻击
- 14个重要特征 : 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 12, 29, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 40
- 去除高相关性特征, 留下6个特征 : 2, 5, 29, 33, 34, 35
R2L攻击
- 18个重要特征 : 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 10, 12, 14, 16, 24, 32, 33, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 41
- 去除高相关性特征, 留下6个特征 : 1, 3, 5, 10, 24, 33
U2R攻击
- 8个重要的特征 : 3, 5, 6, 10, 14, 17, 32, 33
- 去除高相关性特征, 留下5个特征 : 5, 6, 10, 17, 33
NSL-KDD
关于NSL-KDD数据集的准确率
在NSL-KDD原始论文里面(Tavallaee, Mahbod, et al. "A detailed analysis of the KDD CUP 99 data set." 2009 IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence for Security and Defense Applications. IEEE,2009.),作者比较过他的数据集在不同算法下的表现,有一些参考意义,把分类的准确率放在下面。(原文只进行二分类,即正常流量与异常流量)
在KDDTest+上的准确率,大概70-80%。
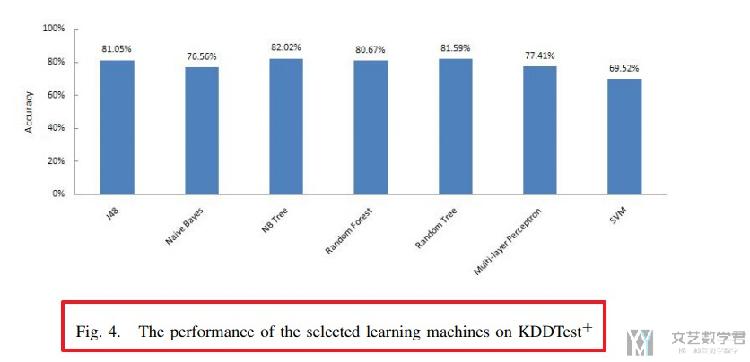
在KDDTest-21上的准确率,大概50-60%。
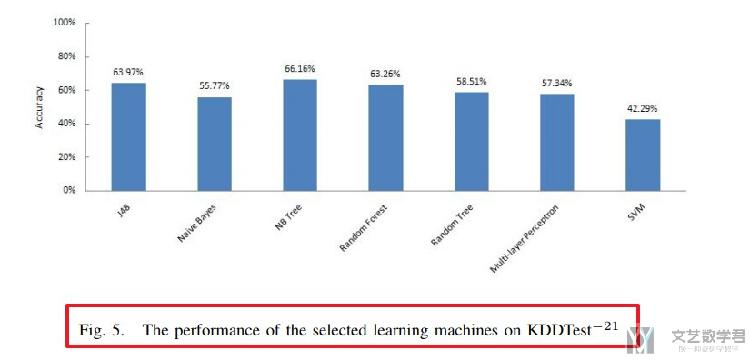
可能存在的疑惑
- Why does the dataset have 43 columns?(为什么数据集有43列)
Maybe too late, but still for someone with the same question. In: M. Tavallaee, E. Bagheri, W. Lu, and A. Ghorbani, “A Detailed Analysis of the KDD CUP 99 Data Set,” explains that the last column (numbers between 0-21) are the times being correctly classified for the machine learners (in total 21). Everytime any instance is being correctly classified, his value increases by 1. This value can be easily discharged withouth any problem.
也就是说, 最后一列数字越大, 能被正确分类的个数最多. 即如果最后一列是21,那么能被所有模型正确分类。
一些论文资料
这里放一下使用NSL-KDD数据集的论文的资料, 方便自己之后的查询与使用.
关于一些检测的代码
这个仓库里有一个作者的五篇论文和相关代码 : Network Intrusion Detection KDDCup '99', NSL-KDD and UNSW-NB15
对NSL-KDD每一个特征的解释
- @article{dhanabal2015study,
- title={A study on NSL-KDD dataset for intrusion detection system based on classification algorithms},
- author={Dhanabal, L and Shantharajah, SP},
- journal={International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer and Communication Engineering},
- volume={4},
- number={6},
- pages={446--452},
- year={2015}
- }

对NSL-KDD每一种攻击详细介绍
- @inproceedings{mahoney2002learning,
- title={Learning nonstationary models of normal network traffic for detecting novel attacks},
- author={Mahoney, Matthew V and Chan, Philip K},
- booktitle={Proceedings of the eighth ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining},
- pages={376--385},
- year={2002},
- organization={ACM}
- }
这个应该是有48页的.

对攻击结果进行解释
- M. Wang, K. Zheng, Y. Yang and X. Wang, "An Explainable Machine Learning Framework for Intrusion Detection Systems," in IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 73127-73141, 2020, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2988359.
不要脸的放一下自己的一篇, 对模型的结果做出解释(欢迎大家引用)。该方法不仅识别出是哪一种攻击,还可以结合特征,验证判断的依据是否和这个攻击的本质是一样的。关于模型解释相关的内容,可以参考链接,模型解释–SHAP Value的简单介绍
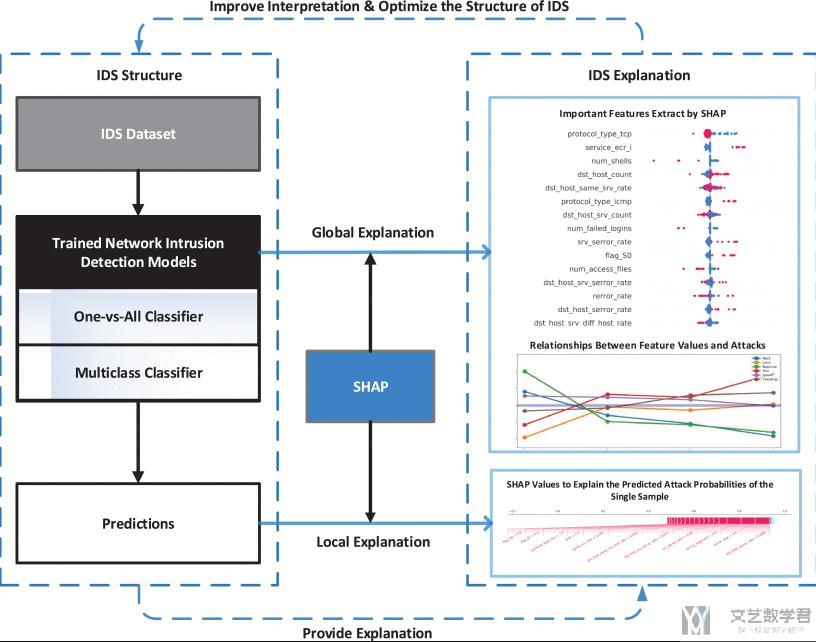
NSL-KDD数据分析
这里放一些其他人做的对于NSL-KDD数据集的分析的工作。可以大致参考一下他们分析的方法和最后的结果,都是notebook的形式,可以直接在线进行查看。
- Modelling Intrusion Detection: Analysis of a Feature Selection Mechanism
- Anomaly-ReactionRL-NSL-KDD
- Kaggle上的一个笔记 : 入侵检测分类由jinner
结语
我自己也写过一些关于入侵检测相关的论文,欢迎大家提出意见(如果有帮助,欢迎引用):
- An explainable machine learning framework for intrusion detection systems
- CENTIME: A Direct Comprehensive Traffic Features Extraction for Encrypted Traffic Classification
- An Encrypted Traffic Classification Framework Based on Convolutional Neural Networks and Stacked Autoencoders

- 微信公众号
- 关注微信公众号
-

- QQ群
- 我们的QQ群号
-













2020年10月16日 下午5:30 1F
喜欢最后《寻找天堂》的图片
2021年4月19日 下午8:30 2F
请问dst_host_count. 前100个连接中,与当前连接具有相同目标主机的连接数,连续,[0, 255]?计算前100个连接相同的数量,为什么范围是[0,255]
2021年4月20日 上午10:43 B1
@ guagua 你好,你这个问题非常好啊,我也没注意到。我看了一下论文,里面对特征的描述是没有「前 100 个连接」这个限制的。你可以对照实际数据集再看一下,这个特征的取值范围。
2021年4月20日 下午7:50 B2
@ 王 茂南 谢谢!!
2021年4月22日 下午5:01 B3
@ guagua 要是你验证了最后的结果,可以在这里留言一下,这几个特征的范围。
2021年5月13日 下午8:10 B4
@ 王 茂南 王兄,目前我在5分类调参怎么都达不到好的效果,请问目前这个NSL-KDD的5分类问题做的最好的模型是什么?能否提供一个源代码?感激不尽。
2021年5月13日 下午10:21 B4
@ hanhan 你好,这可能是因为测试集中包含训练集中没有的流量。但是结果不会太差,我就用普通的全连接网络,准确率可以到 80 左右。
2021年5月14日 下午12:17 B4
@ 王 茂南 主要我是看一些文章宣称最后5分类准确率可达96-98%这个样子我就惊了,实在不知道怎么调出这个玩意。
2021年5月26日 下午12:34 B4
@ hanhan 应该没这么高,我在 NSL-KDD 上只有 80 多,不过我最近毕业了,不做这块了。不过,我这里拉了一个群,里面都是关于做流量检测的,要是你有兴趣,你可以把你的微信号发在我的邮箱,wangmaonan@bupt.edu.cn。
2021年4月20日 下午7:57 3F
再请问一下,这个数据集看起来都是面向连接的网络数据,有没有面向IP流的训练集,我看很多论文都是选用面向流的特征!!谢谢
2021年4月22日 下午4:59 B1
@ guagua 你好,我看过的几个数据集,包括 NSL-KDD,UNSW-NB15,ISCXVPN2016 都是面向连接的(好像有人做过实验,面向连接的效果会好)。但是这些数据集都给了原始数据,你可以自己处理,我是使用 SplitCap.exe 进行处理的,你可以看一下我的这个仓库,https://github.com/wmn7/Traffic-Classification
2021年4月22日 下午9:17 B2
@ 王 茂南 可以加您个练习方式嘛,我是个在读本科生,有好多不懂的问题。请问有那种更完整的DDoS攻击检测数据集吗,包括真实的IP地址,因为我看到很多论文对于DDoS攻击都是默认有大量伪造IP地址和端口,但我下载了很多数据集CIC-IDS-2018、CIC-IDS-2017等等,有的缺IP地址,有的不缺IP地址但攻击地址单一,谢谢!!
2021年4月23日 上午11:49 B3
@ guagua 可以的,你把你的联系方式邮箱发给我吧,邮箱是 wangmaonan@bupt.edu.cn
2021年5月3日 下午12:35 B4
@ 王 茂南 你好,这是我目前看到过的对kdd这个数据集介绍最详细的博客了,请问你是做这个方向的吗?可以加个联系方式请教一下吗?
2021年5月3日 下午3:01 B4
@ beginner001 你好,感谢你的认可。我是做这方面的,主要就是流量检测。你可以把联系方式邮箱发给我,邮箱是 wangmaonan@bupt.edu.cn。
2021年5月4日 下午9:13 B4
@ 王 茂南 联系方式已发到邮箱
2021年5月13日 下午10:48 4F
另外请教一下,我肉眼观察以及使用t-sne算法得到unsw数据集中一些异常特征存在特征完全一致的情况,请问这种情况下不同异常的原始数据是否包含可识别出该异常的特征?
2021年5月14日 下午7:19 5F
我想请问一下,具体的攻击类型有对应具体的特征吗
2021年5月26日 下午12:32 B1
@ 张颖 有一些论文是做特征筛选的,对于特定的攻击选取特定的论文,你可以看下。(另外,我这里拉了一个群,都是关于做流量检测的,要是你有兴趣,你可以把你的微信号发在我的邮箱,wangmaonan@bupt.edu.cn)
2021年5月21日 下午4:46 6F
你好,想问一下,每行数据后面的那个0-21之间的数指的是预测正确的模型个数吗?是可以不需要的数据吗?谢谢!!
2021年5月26日 下午12:18 B1
@ hg123 是的。原文作者使用了多个模型来进行分类,后面的数字表示被多少模型分类正确的。(另外,我这里拉了一个群,都是关于做流量检测的,要是你有兴趣,你可以把你的微信号发在我的邮箱,wangmaonan@bupt.edu.cn)
2021年7月19日 下午4:29 7F
博主你好!看了您的文章受益匪浅,能不能加您好友,一起讨论关于流量监测的问题?
2021年7月21日 下午5:54 B1
@ 书剑一笑 你好,可以的。你可以发邮件到 wangmaonan@bupt.edu.cn,我们有个群,可以一起讨论。
2021年8月10日 上午10:12 B2
@ 王 茂南 你好博主,我有些问题想问下您,能方便加个联系方式吗
2021年8月10日 上午11:36 B3
@ XIEWEI 你好,已经邮件回复你了。